Android - 测试
Android 框架包括一个集成测试框架,可帮助您测试应用程序的所有方面,而 SDK 工具包括用于设置和运行测试应用程序的工具。 无论您是在 Eclipse 中使用 ADT 工作还是从命令行工作,SDK 工具都可以帮助您在模拟器或目标设备中设置和运行测试。
测试结构
Android 的构建和测试工具假定测试项目被组织成测试、测试用例类、测试包和测试项目的标准结构。
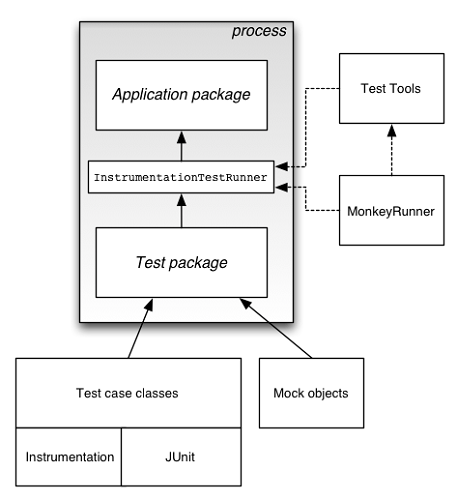
android 中的测试工具
有许多工具可用于测试 android 应用程序。 有些是官方的,如 Junit、Monkey,有些是可用于测试 android 应用程序的第三方工具。 在本章中,我们将解释这两个测试 android 应用程序的工具。
- JUnit
- Monkey
JUnit
您可以使用 JUnit TestCase 类对不调用 Android API 的类进行单元测试。 TestCase 也是 AndroidTestCase 的基类,您可以使用它来测试与 Android 相关的对象。 除了提供 JUnit 框架外,AndroidTestCase 还提供了特定于 Android 的设置、拆卸和辅助方法。
为了使用TestCase,用TestCase 类扩展你的类并实现一个方法调用setUp()。 它的语法如下 −
public class MathTest extends TestCase {
protected double fValue1;
protected double fValue2;
protected void setUp() {
fValue1= 2.0;
fValue2= 3.0;
}
}
对于每个测试,实现一个与夹具交互的方法。 使用布尔值调用 assertTrue(String, boolean) 指定的断言验证预期结果。
public void testAdd() {
double result= fValue1 + fValue2;
assertTrue(result == 5.0);
}
断言方法将您期望的测试值与实际结果进行比较,如果比较失败则抛出异常。
一旦定义了方法,您就可以运行它们。 它的语法如下 −
TestCase test= new MathTest("testAdd");
test.run();
Monkey
UI/Application Exerciser Monkey,通常称为"monkey",是一种命令行工具,可将击键、触摸和手势的伪随机流发送到设备。 您可以使用 Android 调试桥 (adb) 工具运行它。
您可以使用它对应用程序进行压力测试并报告遇到的错误。 您可以通过每次使用相同的随机数种子运行该工具来重复事件流。
Monkey 功能
Monkey 有很多特点,但都可以归结为这四类。
- 基本配置选项
- 操作限制
- 事件类型和频率
- 调试选项
Monkey 用法
为了使用 monkey,打开命令提示符并导航到以下目录。
android ->sdk ->platform-tools
进入目录后,将您的设备与 PC 连接,然后运行以下命令。
adb shell monkey -p your.package.name -v 500
该命令可以分解为这些步骤。
- adb - Android 调试桥。 一种用于从台式机或笔记本电脑连接 Android 手机并向其发送命令的工具。
- shell - shell 只是设备上的一个接口,可以将我们的命令转换为系统命令。
- monkey - monkey 是测试工具。
- v - v 代表详细方法。
- 500- 它是要发送以进行测试的频率 conut 或事件数。
这也显示在图中 −
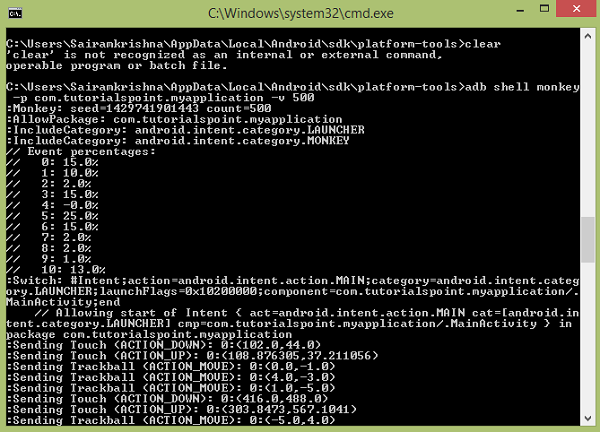
在上面的命令中,您在默认的 android UI 应用程序上运行 monkey 工具。 现在为了将它运行到您的应用程序中,您必须执行以下操作。
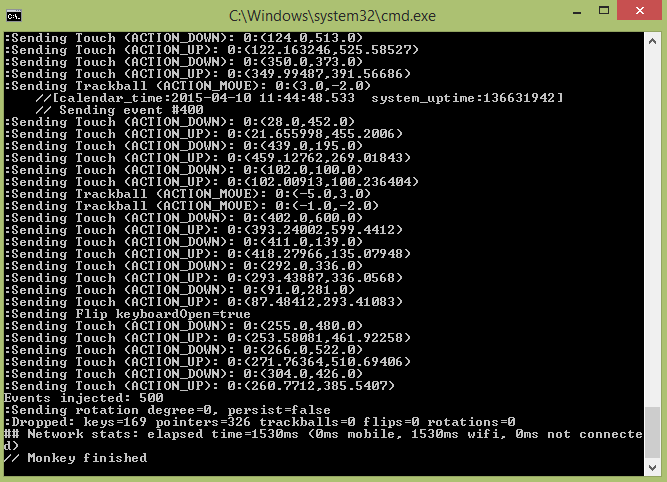
最后你会完成如下所示
下图也显示了这一点。 通过键入此命令,您实际上生成了 500 个随机事件进行测试。
示例
以下示例演示了测试的使用。 它创建了一个可用于 monkey 的基本应用程序。
为了试验这个例子,你需要在一个实际的设备上运行它,然后按照开头解释的 monkey 步骤。
| 步骤 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 您将使用 Android Studio 在 com.tutorialspoint.myapplication 包下创建一个 Android 应用程序。 |
| 2 | 修改 src/MainActivity.java 文件添加活动代码。 |
| 3 | 修改 layouta XML 文件 res/layout/activity_main.xml 如果需要,添加任何 GUI 组件。 |
| 4 | 创建 src/second.java 文件以添加活动代码。 |
| 5 | 修改布局 XML 文件 res/layout/view.xml 如果需要,添加任何 GUI 组件。 |
| 6 | 运行应用程序并选择一个正在运行的 android 设备并在其上安装应用程序并验证结果。 |
这是MainActivity.java的内容。
package com.tutorialspoint.myapplication;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
Button b1;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
b1=(Button)findViewById(R.id.button);
}
public void button(View v){
Intent in =new Intent(MainActivity.this,second.class);
startActivity(in);
}
}
这是second.java的内容。
package com.tutorialspoint.myapplication;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class second extends Activity{
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.view);
Button b1=(Button)findViewById(R.id.button2);
b1.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Toast.makeText(second.this,"Thanks",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
}
}
这是activity_main.xml 的内容。
In the below code abc indicates the logo of tutorialspoint.com
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="UI Animator Viewer"
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:textSize="25sp"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Tutorials point"
android:id="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_below="@+id/textView"
android:layout_alignRight="@+id/textView"
android:layout_alignEnd="@+id/textView"
android:textColor="#ff36ff15"
android:textIsSelectable="false"
android:textSize="35dp" />
<ImageView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/imageView"
android:src="@drawable/abc"
android:layout_below="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button"
android:onClick="button"
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_below="@+id/imageView"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="100dp" />
</RelativeLayout>
这是view.xml
的内容
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="button"
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Tutorials point "
android:id="@+id/textView3"
android:textColor="#ff3aff22"
android:textSize="35dp"
android:layout_above="@+id/button2"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginBottom="90dp" />
</RelativeLayout>
这是Strings.xml的内容。
<resources> <string name="app_name">My Application</string> </resources>
这是AndroidManifest.xml的内容。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.tutorialspoint.myapplication" >
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<activity android:name=".second"></activity>
</application>
</manifest>
让我们尝试运行您的 Android 测试应用程序。我假设您已将实际的 Android 移动设备与您的计算机连接起来。 要从 Android Studio 运行应用程序,请打开项目的活动文件之一,然后单击工具栏中的 Run  图标。在启动您的应用程序之前,Android Studio 将显示以下窗口以选择您要运行 Android 应用程序的选项。
图标。在启动您的应用程序之前,Android Studio 将显示以下窗口以选择您要运行 Android 应用程序的选项。
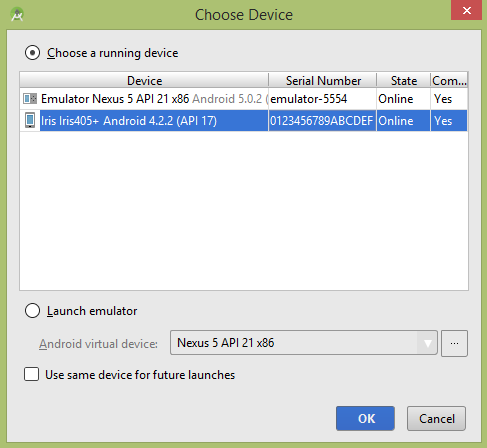
选择您的移动设备作为选项,然后检查将显示应用程序屏幕的移动设备。 现在只需按照 monkey 部分顶部提到的步骤来执行此应用程序的测试。

