Spring - Hello World 示例
让我们开始使用 Spring 框架进行实际编程。 在你开始使用 Spring 框架编写你的第一个示例之前,你必须确保你已经按照 Spring - 环境安装设置章节中的说明正确设置了你的 Spring 环境。我们还假设您对 Eclipse IDE 有一定的工作知识。
现在让我们继续编写一个简单的 Spring 应用程序,它将打印"Hello World!" 或基于 Spring Beans 配置文件中完成的配置的任何其他消息。
步骤 1 - 创建 Java 项目
第一步是使用 Eclipse IDE 创建一个简单的 Java 项目。 按照选项 File → New → Project,最后从向导列表中选择 Java Project 向导。 现在使用向导窗口将您的项目命名为 HelloSpring,如下所示 −
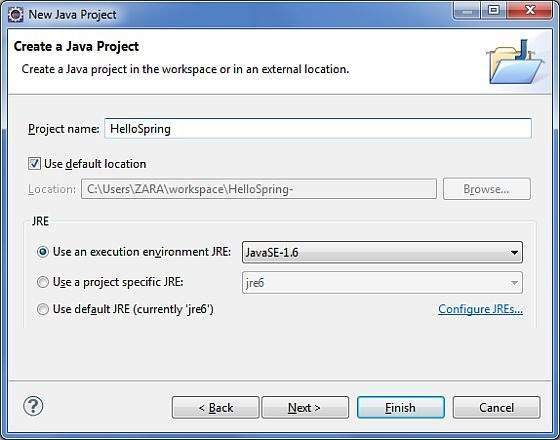
成功创建项目后,您的 Project Explorer 中将包含以下内容 −
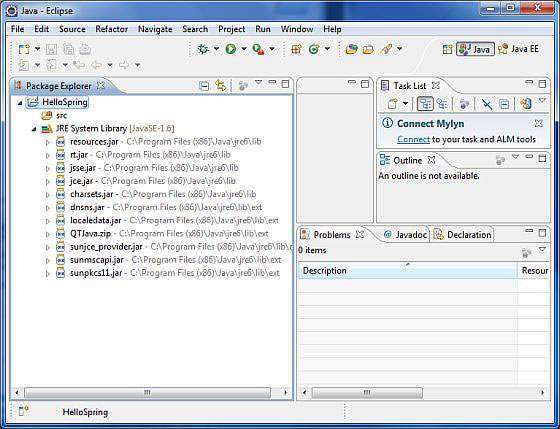
步骤 2 -添加所需的库
第二步,让我们在项目中添加 Spring 框架和通用日志记录 API 库。 为此,请右键单击您的项目名称 HelloSpring,然后按照上下文菜单中的以下选项进行操作 − Build Path → Configure Build Path 如下所示显示 Java 构建路径窗口 −
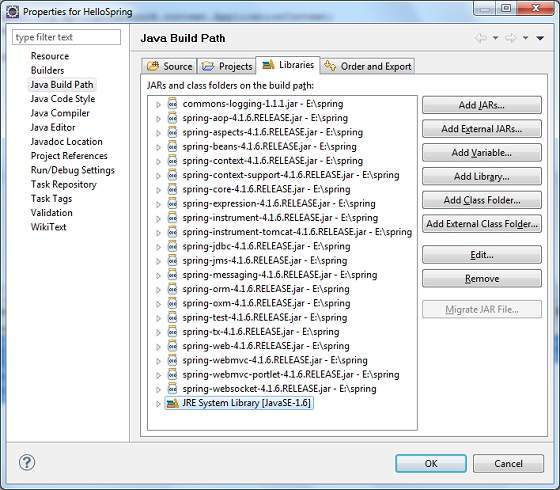
现在使用 Libraries 选项卡下的 Add External JARs 按钮从 Spring 框架和 Common Logging 安装目录添加以下核心 JAR −
commons-logging-1.1.1
spring-aop-4.1.6.RELEASE
spring-aspects-4.1.6.RELEASE
spring-beans-4.1.6.RELEASE
spring-context-4.1.6.RELEASE
spring-context-support-4.1.6.RELEASE
spring-core-4.1.6.RELEASE
spring-expression-4.1.6.RELEASE
spring-instrument-4.1.6.RELEASE
spring-instrument-tomcat-4.1.6.RELEASE
spring-jdbc-4.1.6.RELEASE
spring-jms-4.1.6.RELEASE
spring-messaging-4.1.6.RELEASE
spring-orm-4.1.6.RELEASE
spring-oxm-4.1.6.RELEASE
spring-test-4.1.6.RELEASE
spring-tx-4.1.6.RELEASE
spring-web-4.1.6.RELEASE
spring-webmvc-4.1.6.RELEASE
spring-webmvc-portlet-4.1.6.RELEASE
spring-websocket-4.1.6.RELEASE
步骤 3 - 创建源文件
现在让我们在 HelloSpring 项目下创建实际的源文件。 首先,我们需要创建一个名为 com.tutorialspoint 的包。为此,请在包资源管理器部分中右键单击 src 并遵循选项 − New → Package。
接下来我们将在 com.tutorialspoint 包下创建 HelloWorld.java 和 MainApp.java 文件。
这是 HelloWorld.java 文件的内容 −
package com.tutorialspoint;
public class HelloWorld {
private String message;
public void setMessage(String message){
this.message = message;
}
public void getMessage(){
System.out.println("Your Message : " + message);
}
}
下面是第二个文件MainApp.java的内容 −
package com.tutorialspoint;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml");
HelloWorld obj = (HelloWorld) context.getBean("helloWorld");
obj.getMessage();
}
}
主程序需要注意以下两个要点 −
第一步是在我们使用框架 API ClassPathXmlApplicationContext() 的地方创建应用程序上下文。 此 API 加载 bean 配置文件,并最终基于提供的 API,它负责创建和初始化所有对象,即配置文件中提到的 bean。
第二步用于使用创建的上下文的 getBean() 方法获取所需的 bean。 该方法使用 bean ID 返回一个通用对象,最终可以转换为实际对象。 一旦有了对象,就可以使用该对象调用任何类方法。
步骤 4 - 创建 Bean 配置文件
您需要创建一个 Bean 配置文件,该文件是一个 XML 文件,充当将 bean (即类)粘合在一起的粘合剂。 该文件需要在 src 目录下创建,如下图所示 −
通常开发人员将此文件命名为 Beans.xml,但您可以自行选择任何您喜欢的名称。 您必须确保该文件在 CLASSPATH 中可用,并在主应用程序中使用相同的名称,同时创建一个应用程序上下文,如 MainApp.java 文件中所示。
Beans.xml 用于将唯一 ID 分配给不同的 bean,并控制具有不同值的对象的创建,而不会影响任何 Spring 源文件。 例如,使用以下文件,您可以为"message"变量传递任何值,并且可以打印不同的消息值,而不会影响 HelloWorld.java 和 MainApp.java 文件。 让我们看看它是如何工作的 −
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd">
<bean id = "helloWorld" class = "com.tutorialspoint.HelloWorld">
<property name = "message" value = "Hello World!"/>
</bean>
</beans>
当 Spring 应用程序被加载到内存中时,框架使用上述配置文件来创建所有定义的 bean,并为它们分配一个唯一的 ID,如 <bean> 标记中定义的那样。您可以使用 <property> 标签来传递在创建对象时使用的不同变量的值。
步骤 5 -运行程序
一旦您完成了源和 bean 配置文件的创建,您就可以开始这一步,即编译和运行程序。 为此,请保持 MainApp.Java 文件选项卡处于活动状态并使用 Eclipse IDE 中可用的 Run 选项或使用 Ctrl + F11 编译并运行您的 MainApp 应用程序。 如果您的应用程序一切正常,则会在 Eclipse IDE 的控制台中打印以下消息 −
Your Message : Hello World!
恭喜,您已成功创建第一个 Spring 应用程序。 您可以通过更改"message"属性的值并保持两个源文件不变来看到上述 Spring 应用程序的灵活性。

